What is the rhythmic pattern pictured below? This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of rhythmic patterns, providing a thorough understanding of their elements, identification, notation, analysis, and applications. Embark on a journey to decipher the rhythmic complexities that underpin music, dance, and beyond.
From the fundamental concepts of beat, tempo, and meter to the techniques for identifying and analyzing rhythmic patterns, this guide equips readers with the tools to unravel the rhythmic tapestry that surrounds us.
1. Rhythmic Pattern Overview

Rhythmic patterns refer to the organized sequence of beats and rests in music. They form the backbone of musical structure, providing a sense of time, motion, and flow.
Key elements of rhythmic patterns include:
- Beat:The basic unit of time in music, providing the steady pulse.
- Tempo:The speed at which the beats occur, measured in beats per minute (BPM).
- Meter:The grouping of beats into regular patterns, creating a sense of rhythm.
2. Identifying Rhythmic Patterns
Identifying rhythmic patterns involves:
- Determining the beat:Listening for the underlying pulse and counting the beats.
- Measuring the tempo:Using a metronome or counting the beats over a specific time period.
- Analyzing the meter:Grouping the beats into regular patterns, typically based on multiples of two or three.
Common rhythmic patterns include:
- Duple meter:Two beats per measure (e.g., march, rock)
- Triple meter:Three beats per measure (e.g., waltz, tango)
- Quadruple meter:Four beats per measure (e.g., pop, country)
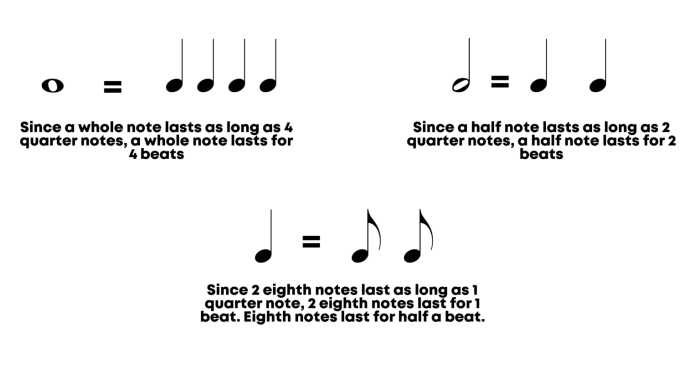
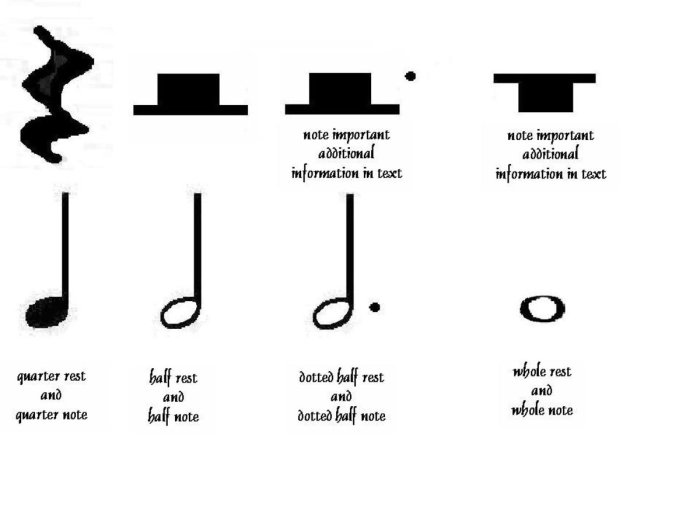
3. Notation and Representation, What is the rhythmic pattern pictured below
Rhythmic patterns can be notated using various systems:
- Musical notation:Symbols on a musical staff representing the duration of notes and rests.
- Rhythmic symbols:Non-staff notation using symbols to indicate beats, rests, and their durations.
| Notation System | Example |
|---|---|
| Musical notation |  |
| Rhythmic symbols |  |
4. Analysis of Rhythmic Patterns
Analyzing rhythmic patterns involves:
- Identifying characteristics:Describing the pattern’s beat, tempo, meter, and any variations.
- Classifying patterns:Grouping patterns based on their characteristics, such as duple, triple, or syncopated.
Examples of rhythmic patterns with varying characteristics:
- Simple duple:Steady beat with two equal beats per measure.
- Compound triple:Three beats per measure, with each beat subdivided into two.
- Syncopated rhythm:Accents placed on off-beats, creating a sense of anticipation.
5. Rhythmic Patterns in Music
Rhythmic patterns play a crucial role in music:
- Structure and organization:Providing a framework for musical sections and transitions.
- Mood and emotion:Evoking different emotions through variations in tempo, meter, and syncopation.
- Cultural influences:Reflecting the rhythms and beats of specific cultures and musical genres.
Examples of rhythmic patterns in different musical genres:
- Classical:Complex and intricate rhythmic patterns with frequent syncopation.
- Jazz:Syncopated rhythms, improvisation, and off-beat accents.
- Rock:Driving and steady rhythms, often based on duple or quadruple meter.
6. Applications of Rhythmic Patterns
Rhythmic patterns have practical applications beyond music:
- Dance:Coordinating movements and creating a sense of rhythm.
- Sports:Timing and coordination in activities such as running, jumping, and martial arts.
- Industrial processes:Synchronizing machinery and ensuring smooth operations.
Understanding rhythmic patterns enhances coordination, timing, and efficiency in various activities.
Detailed FAQs: What Is The Rhythmic Pattern Pictured Below
What are the key elements of a rhythmic pattern?
The key elements of a rhythmic pattern include beat, tempo, and meter.
How can I identify the rhythmic pattern in a piece of music?
To identify the rhythmic pattern, listen for the beat, determine the tempo, and analyze the grouping of beats into measures.
What is the purpose of rhythmic notation?
Rhythmic notation provides a visual representation of rhythmic patterns, allowing musicians to read and perform them accurately.