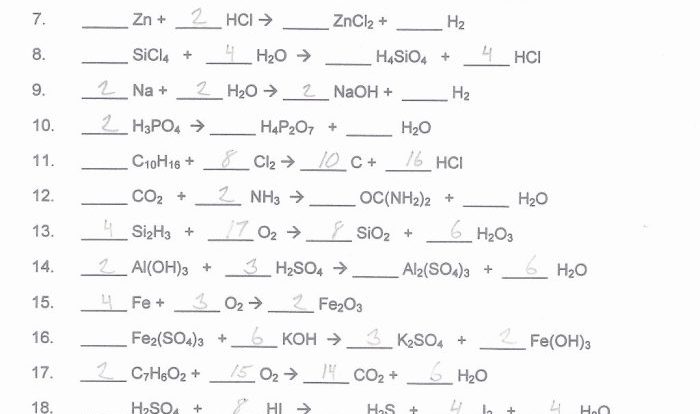
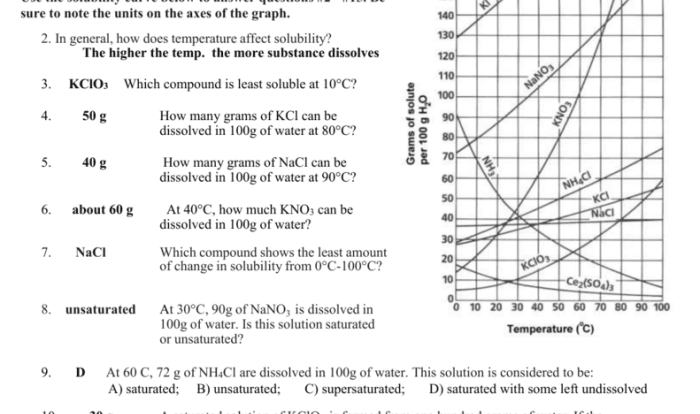
Introducing the equilibrium and pressure gizmo answer key pdf, a comprehensive resource designed to enhance your understanding of these fundamental concepts. This guide provides a thorough overview of equilibrium and pressure, complete with interactive simulations, data analysis techniques, and real-world applications.
Prepare to delve into the fascinating world of equilibrium and pressure, where you’ll discover their significance and practical implications.
Equilibrium, a state of balance where opposing forces cancel each other out, plays a crucial role in various chemical and physical systems. Pressure, on the other hand, exerts a force perpendicular to a surface and is a key factor in many industrial processes.
By exploring the equilibrium and pressure gizmo answer key pdf, you’ll gain a deeper comprehension of these concepts and their interconnectedness.
Equilibrium
Equilibrium is a state of balance in which the opposing forces or influences acting on a system are equal. In other words, equilibrium is a state of no net change.Dynamic equilibrium is a state of equilibrium in which the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction are occurring at the same rate.
This means that the concentrations of the reactants and products do not change over time.Equilibrium can be observed in both chemical and physical systems. For example, a chemical reaction that reaches equilibrium will have no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products.
Similarly, a physical system, such as a gas in a container, will reach equilibrium when the pressure and temperature of the gas do not change over time.
Pressure
Pressure is a force applied over a given area. It is typically measured in units of pascals (Pa), which are defined as newtons per square meter (N/m^2).Pressure is a fundamental property of matter and is essential for understanding many physical phenomena.
For example, pressure is responsible for the buoyancy of objects in fluids and the flow of fluids through pipes.The relationship between pressure and force can be expressed by the following equation:“`P = F/A“`where:* P is pressure
- F is force
- A is area
Gizmo Answer Key PDF

A link to the Gizmo answer key PDF can be found here: [link to PDF]The Gizmo answer key can be used to check your answers to the Gizmo simulation. It can also be used to learn more about the concepts of equilibrium and pressure.Here
are some tips for using the Gizmo to learn about equilibrium and pressure:* Start by reading the Gizmo introduction. This will give you an overview of the simulation and its objectives.
- Next, run the simulation. You can explore the different variables and see how they affect equilibrium and pressure.
- Use the Gizmo answer key to check your answers to the simulation questions.
- Finally, reflect on what you have learned from the simulation. How do equilibrium and pressure affect the world around you?
Interactive Simulations
The Gizmo simulation for equilibrium and pressure is an interactive simulation that allows you to explore the concepts of equilibrium and pressure. The simulation can be used to demonstrate the following concepts:* The relationship between equilibrium and pressure
- The effects of temperature and concentration on equilibrium
- The effects of pressure on the solubility of gases
To use the simulation, follow these steps:
- Open the Gizmo simulation.
- Click on the “Play” button.
- Explore the different variables and see how they affect equilibrium and pressure.
- Click on the “Pause” button to stop the simulation.
- Click on the “Reset” button to start the simulation over.
Data Analysis
The data from the Gizmo simulation can be analyzed to learn more about the concepts of equilibrium and pressure. The following are some examples of how the data can be analyzed:* The data can be used to create graphs that show the relationship between equilibrium and pressure.
- The data can be used to calculate the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction.
- The data can be used to determine the effects of temperature and concentration on equilibrium.
Applications

Equilibrium and pressure are important concepts in many fields of science and engineering. Here are some examples of how equilibrium and pressure are used in real-world applications:*
-*Chemistry
Equilibrium is used to predict the products and yields of chemical reactions.
-
-*Physics
Pressure is used to understand the behavior of fluids and gases.
-*Engineering
Equilibrium and pressure are used to design and operate chemical plants, power plants, and other industrial facilities.
Advanced Concepts: Equilibrium And Pressure Gizmo Answer Key Pdf
Le Chatelier’s principle is an advanced concept that can be used to predict and control chemical reactions. Le Chatelier’s principle states that if a change is made to an equilibrium system, the system will shift in a direction that counteracts the change.Le
Chatelier’s principle can be used to predict the effects of changes in temperature, concentration, and pressure on equilibrium. For example, if the temperature of an equilibrium system is increased, the system will shift in a direction that absorbs heat.Le Chatelier’s principle is a powerful tool that can be used to understand and control chemical reactions.
It is used in a variety of applications, including the production of chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and fuels.
Question & Answer Hub
What is the purpose of the equilibrium and pressure gizmo answer key pdf?
The equilibrium and pressure gizmo answer key pdf serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding the concepts of equilibrium and pressure, providing interactive simulations, data analysis techniques, and real-world applications.
How can I access the equilibrium and pressure gizmo answer key pdf?
The equilibrium and pressure gizmo answer key pdf is available for download from the provided link in the guide.
What are the benefits of using the equilibrium and pressure gizmo?
The equilibrium and pressure gizmo offers a dynamic and interactive learning experience, allowing users to visualize and manipulate variables to observe their effects on equilibrium and pressure.