Iron III nitrate and potassium thiocyanate, two remarkable compounds, take center stage in this exploration that delves into their properties, reactivity, applications, safety considerations, and related chemistry. With meticulous attention to detail, we embark on a journey that unveils the intricacies of these substances, unraveling their significance in various scientific and industrial domains.
As we delve into the fascinating world of iron III nitrate and potassium thiocyanate, we uncover their unique characteristics, examining their physical and chemical properties. Their appearance, odor, solubility, and stability are meticulously described, providing a comprehensive understanding of their fundamental nature.
Iron(III) Nitrate and Potassium Thiocyanate: Iron Iii Nitrate And Potassium Thiocyanate

Iron(III) nitrate and potassium thiocyanate are two inorganic compounds with distinct properties and applications. This article will explore their physical and chemical characteristics, reactivity, applications, safety considerations, and related compounds.
Properties and Characteristics, Iron iii nitrate and potassium thiocyanate
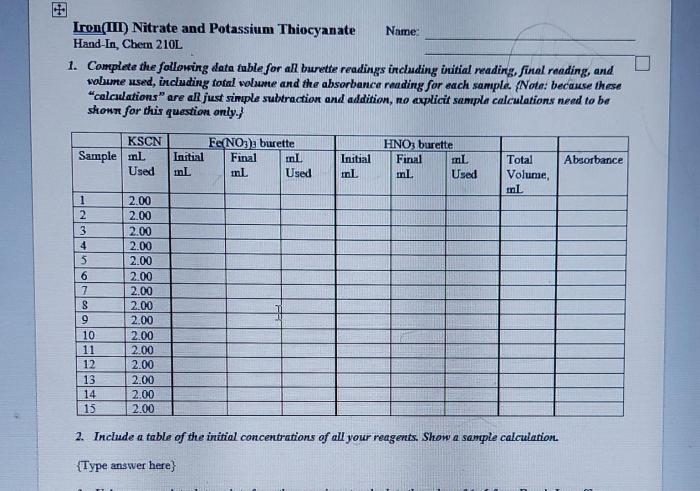
The physical and chemical properties of iron(III) nitrate and potassium thiocyanate are summarized in the following table:
| Property | Iron(III) Nitrate | Potassium Thiocyanate |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Yellow-brown solid | Colorless crystals |
| Odor | Odorless | Odorless |
| Solubility in water | Highly soluble | Highly soluble |
| Stability | Stable in dry air | Stable in dry air |
Iron(III) nitrate is a hygroscopic compound that absorbs moisture from the air, while potassium thiocyanate is a deliquescent compound that absorbs moisture and dissolves in it.
Reactivity and Reactions
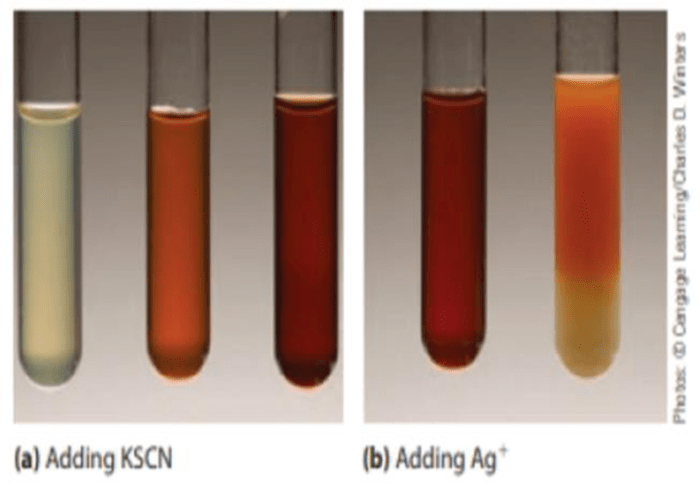
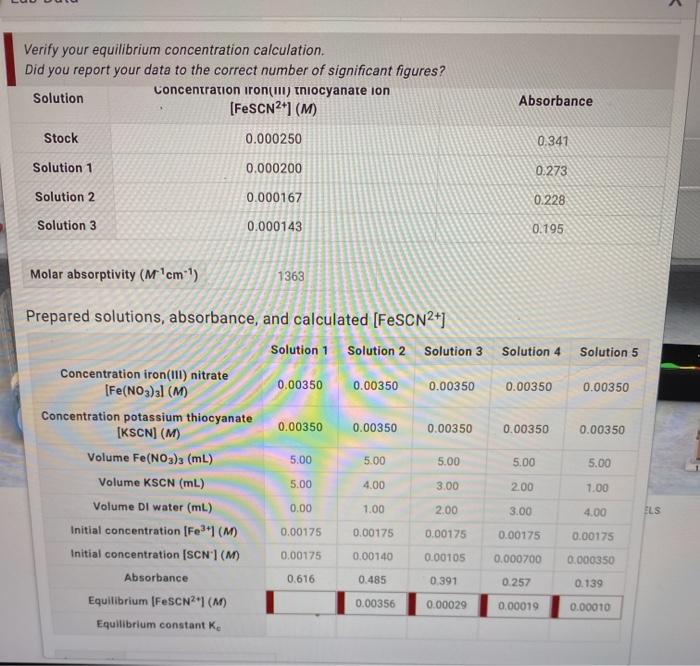
When iron(III) nitrate and potassium thiocyanate are combined in an aqueous solution, a chemical reaction occurs. The reaction produces iron(III) thiocyanate, which is a deep red-colored compound. The reaction can be represented by the following equation:
Fe(NO3) 3(aq) + 3KSCN(aq) → Fe(SCN) 3(aq) + 3KNO 3(aq)
The reaction is exothermic, meaning that it releases heat. The rate of the reaction can be affected by factors such as temperature, concentration, and the presence of a catalyst.
Applications and Uses
Iron(III) nitrate is used in a variety of industrial and laboratory applications. It is used as a mordant in the dyeing of textiles, as a coagulant in water treatment, and as a fertilizer in agriculture. Potassium thiocyanate is used in photography, analytical chemistry, and metallurgy.
- Industrial applications:Iron(III) nitrate is used in the production of steel, fertilizers, and dyes. Potassium thiocyanate is used in the production of photographic chemicals, analytical reagents, and metalworking fluids.
- Laboratory applications:Iron(III) nitrate is used as a reagent in analytical chemistry, while potassium thiocyanate is used as a titrant in volumetric analysis.
Safety and Handling
Iron(III) nitrate and potassium thiocyanate are both toxic compounds. They should be handled with care and appropriate safety precautions should be taken.
- Inhalation:Inhalation of iron(III) nitrate or potassium thiocyanate can cause irritation of the respiratory tract.
- Skin contact:Contact with iron(III) nitrate or potassium thiocyanate can cause skin irritation.
- Eye contact:Contact with iron(III) nitrate or potassium thiocyanate can cause eye irritation.
- Ingestion:Ingestion of iron(III) nitrate or potassium thiocyanate can cause gastrointestinal distress.
When handling iron(III) nitrate or potassium thiocyanate, it is important to wear gloves, eye protection, and a dust mask. It is also important to work in a well-ventilated area.
Related Compounds and Chemistry
Iron(III) nitrate and potassium thiocyanate are two of many iron(III) and thiocyanate compounds. Other related compounds include:
- Iron(II) nitrate:Iron(II) nitrate is a green-colored solid that is soluble in water. It is used as a reducing agent in chemical reactions.
- Iron(III) chloride:Iron(III) chloride is a brown-colored solid that is soluble in water. It is used as a coagulant in water treatment and as a mordant in the dyeing of textiles.
- Potassium thiocyanate:Potassium thiocyanate is a colorless solid that is soluble in water. It is used in photography, analytical chemistry, and metallurgy.
FAQs
What are the key physical properties of iron III nitrate?
Iron III nitrate is a hygroscopic, reddish-brown solid with a molecular weight of 241.86 g/mol. It is soluble in water and ethanol and has a melting point of 47.2 °C.
What is the chemical formula of potassium thiocyanate?
Potassium thiocyanate has the chemical formula KSCN. It is a white, crystalline solid that is soluble in water and ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 97.18 g/mol.